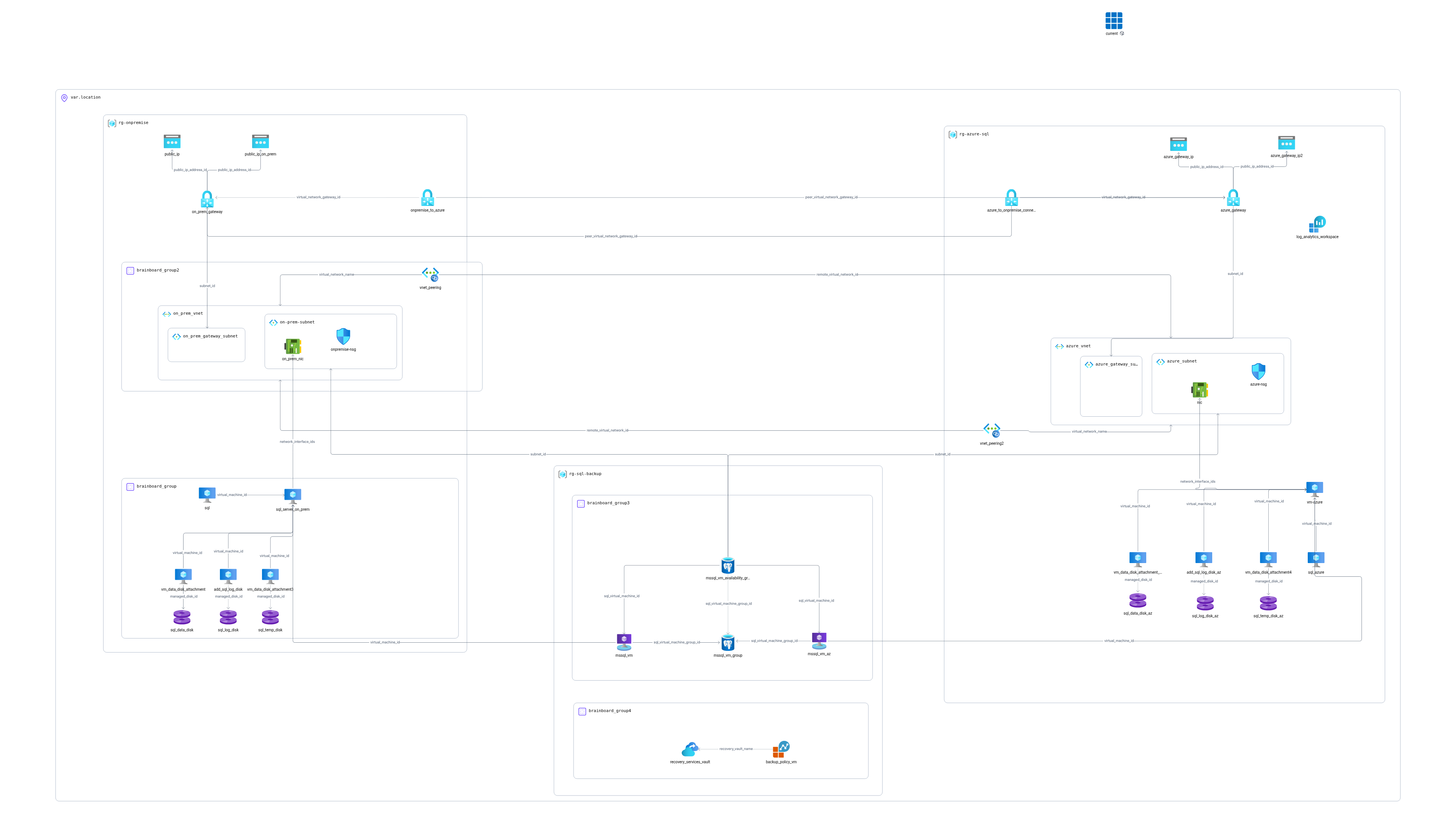
# Hybrid SQL Server Always On Architecture with Azure Site-to-Site VPN
This Terraform configuration deploys a complete Azure infrastructure for SQL Server with high availability, featuring on-premises simulation, VPN connectivity, and Always On Availability Groups across hybrid environments.
## 🏗️ Architecture Overview
This infrastructure creates:
- **Two Virtual Networks**: Simulating on-premises and Azure environments
- **Site-to-Site VPN**: Connecting on-premises to Azure via VPN gateways
- **SQL Server VMs**: Two VMs with SQL Server configured for Always On Availability Groups
- **High Availability**: SQL Server Always On Availability Groups across sites
- **Backup & Recovery**: Azure Recovery Services Vault with VM backup policies
- **Monitoring**: Log Analytics Workspace for centralized logging
## 📋 Prerequisites
- **Azure Subscription** with appropriate permissions
- **Terraform** >= 1.0
- **Azure CLI** installed and configured
- **PowerShell** (for post-deployment SQL configuration)
## 🚀 Quick Start
### 1. Clone and Configure
```bash
git clone
cd azure-sql-infrastructure
```
### 2. Set Variables
Create a `terraform.tfvars` file with your configuration:
```hcl
# Basic Configuration
location = "West Europe"
# Resource Groups
rg_onpremise_name = "rg-onpremise-sql"
rg_azure_name = "rg-azure-sql"
rg_backup_name = "rg-sql-backup"
# Virtual Networks
on_prem_vnet_name = "vnet-onprem"
on_prem_vnet_address_space = "10.0.0.0/16"
azure_vnet_name = "vnet-azure"
azure_vnet_address_space = "10.1.0.0/16"
# Subnets
on_prem_subnet_name = "subnet-onprem"
on_prem_subnet_address = "10.0.0.0/24"
azure_subnet_name = "subnet-azure"
azure_subnet_address = "10.1.0.0/24"
# Gateway Subnets
on_prem_gateway_subnet_address = "10.0.1.0/27"
azure_gateway_subnet_address = "10.1.1.0/27"
# Virtual Machines
on_prem_computer_name = "vm-sql-onprem"
azure_computer_name = "vm-sql-azure"
computer_admin_user = "sqladmin"
admin_password = "YourSecurePassword123!"
# SQL Server Image
computer_src_img_publisher = "MicrosoftSQLServer"
computer_src_img_offer = "sql2019-ws2019"
computer_src_img_sku = "standard"
computer_src_img_ref_ver = "latest"
# Backup Configuration
backup_policy_vm_name = "policy-sql-backup"
backup_policy_vm_time = "23:00"
backup_policy_vm_freq = "Daily"
# Log Analytics
log_analytics_workspace_name = "law-sql-monitoring"
log_analytics_workspace_sku = "PerGB2018"
log_retention_in_days = 30
# Tags
tags = {
Environment = "Production"
Project = "SQL-HA"
Owner = "DBA-Team"
}
```
### 3. Deploy Infrastructure
```bash
# Initialize Terraform
terraform init
# Plan deployment
terraform plan
# Apply configuration
terraform apply
```
## 🔧 Post-Deployment Configuration
### SQL Server Always On Setup
After infrastructure deployment, configure SQL Server Always On Availability Groups:
1. **Connect to both VMs** via RDP
2. **Configure Windows Failover Clustering**
3. **Enable Always On Availability Groups**
4. **Create Availability Group** with databases
```sql
-- Example SQL commands (run on primary replica)
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP [AG_SQLTest]
WITH (
AUTOMATED_BACKUP_PREFERENCE = SECONDARY,
DB_FAILOVER = OFF,
DTC_SUPPORT = NONE
)
FOR DATABASE [YourDatabase]
REPLICA ON
N'VM-SQL-ONPREM' WITH (
ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://vm-sql-onprem:5022',
AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = AUTOMATIC,
SEEDING_MODE = AUTOMATIC
),
N'VM-SQL-AZURE' WITH (
ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://vm-sql-azure:5022',
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL,
SEEDING_MODE = AUTOMATIC
);
```
## 📊 Infrastructure Components
### Resource Groups
- `rg-onpremise-sql`: On-premises simulation resources
- `rg-azure-sql`: Azure cloud resources
- `rg-sql-backup`: Backup and recovery services
### Networking
- **VPN Gateways**: VpnGw2AZ SKU with active-active configuration
- **Public IPs**: Static allocation for gateway connectivity
- **NSGs**: RDP access rules (customize for production)
- **VNet Peering**: Additional connectivity between networks
### Virtual Machines
- **On-Premises VM**: Standard_D3_v2 with SQL Server
- **Azure VM**: Standard_DS3_v2 with SQL Server
- **Managed Disks**: Separate disks for data, logs, and tempdb
### SQL Server Configuration
- **IaaS Extension**: Automated patching and backup
- **Availability Groups**: Multi-subnet configuration
- **Listener**: Port 1433 with multi-subnet IPs
## 🔐 Security Considerations
### Current Security Settings
- RDP access allowed from anywhere (port 3389)
- Hardcoded shared key for VPN connection
- Password visible in configuration
### Production Recommendations
```hcl
# Restrict RDP access
security_rule {
name = "AllowRDP"
priority = 1001
direction = "Inbound"
access = "Allow"
protocol = "Tcp"
source_port_range = "*"
destination_port_ranges = ["3389"]
source_address_prefix = "YOUR_OFFICE_IP/32" # Restrict source
destination_address_prefix = "*"
}
# Use Azure Key Vault for secrets
data "azurerm_key_vault_secret" "admin_password" {
name = "sql-admin-password"
key_vault_id = var.key_vault_id
}
```
## 📈 Monitoring & Backup
### Log Analytics
- Centralized logging workspace
- 30-day retention (configurable)
- Integration with Azure Monitor
### Backup Policy
- Daily VM backups at 23:00
- 7-day retention for daily backups
- Stored in Recovery Services Vault
### Recommended Monitoring
```bash
# Enable SQL Server monitoring
az monitor diagnostic-settings create \
--resource /subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourceGroups/{rg-name}/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/{vm-name} \
--name "SQLServerDiagnostics" \
--workspace /subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourceGroups/{rg-name}/providers/Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/{workspace-name}
```
## 🔧 Troubleshooting
### Common Issues
**VPN Connection Fails**
```bash
# Check gateway status
az network vnet-gateway show --name {gateway-name} --resource-group {rg-name}
# Reset VPN connection
az network vpn-connection reset --name {connection-name} --resource-group {rg-name}
```
**SQL Server Extensions Issues**
```bash
# Check extension status
az vm extension list --vm-name {vm-name} --resource-group {rg-name}
# Reinstall SQL IaaS extension
az vm extension set --vm-name {vm-name} --resource-group {rg-name} --name SqlIaasExtension --publisher Microsoft.SqlServer.Management
```
**Availability Group Listener Issues**
- Verify network connectivity between subnets
- Check Windows Firewall settings
- Validate DNS resolution
## 💰 Cost Optimization
### Current Resource Costs (Estimated)
- **VPN Gateways**: ~$200/month each
- **Virtual Machines**: ~$150-300/month each
- **Managed Disks**: ~$50-100/month total
- **Public IPs**: ~$5/month each
### Optimization Tips
- Use **Basic SKU** for development environments
- Implement **auto-shutdown** for non-production VMs
- Consider **Azure SQL Managed Instance** for simpler management
## 🧹 Cleanup
To destroy all resources:
```bash
terraform destroy
```
**⚠️ Warning**: This will permanently delete all resources and data.
## 📚 Additional Resources
- [Azure SQL Server on VM Best Practices](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/virtual-machines/windows/performance-guidelines-best-practices)
- [Always On Availability Groups](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/availability-groups/windows/overview-of-always-on-availability-groups-sql-server)
- [Terraform Azure Provider](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/azurerm/latest/docs)
## 🤝 Contributing
1. Fork the repository
2. Create a feature branch
3. Make your changes
4. Test thoroughly
5. Submit a pull request
## 📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
---
**Last Updated**: July 2025
**Terraform Version**: >= 1.0
**Azure Provider Version**: >= 3.0
Industries
.webp) HealthcareControl environments and simplify operations
HealthcareControl environments and simplify operations.webp) FinancialFragmentation leads to increased costs, inefficiency and risk
FinancialFragmentation leads to increased costs, inefficiency and risk.webp) RetailUnify financial operations to reduce risk and costs
RetailUnify financial operations to reduce risk and costs TelecommunicationSimplify network complexity and accelerate service delivery
TelecommunicationSimplify network complexity and accelerate service delivery GovernmentSecure, compliant, and efficient cloud adoption for the public sector
GovernmentSecure, compliant, and efficient cloud adoption for the public sector
Use cases
.webp) Move to IaCThe easiest way to move to IaC: Brainboard one click migration.
Move to IaCThe easiest way to move to IaC: Brainboard one click migration..webp) Standardize IaCGive your users a reason to follow your guidelines.
Standardize IaCGive your users a reason to follow your guidelines..webp) Self-serve modelBuild your internal service catalog to easily provision on-demand infrastructure.
Self-serve modelBuild your internal service catalog to easily provision on-demand infrastructure..webp) Lower the learning curveYou don’t need to learn everything at once. Learn by doing.
Lower the learning curveYou don’t need to learn everything at once. Learn by doing..webp) Your Disaster Recovery strategySystems fail, all the time. Plan ahead and protect against the unknown today!
Your Disaster Recovery strategySystems fail, all the time. Plan ahead and protect against the unknown today!
Features
- Smart cloud designerThe power of design combined with the flexibility of code
- Terraform & OpenTofu modulesCentral & single source of truth of your private, public and/or community modules.
- GitOps workflowSmoothly connect your cloud infrastructure with your git repository.
- Drift detection and remediationMonitor and maintain control of any drift between your source of truth and your cloud provider.
- Synchronized architecturesEliminate drift between your environments (dev, QA, staging, prod…)

Brainboard is an AI driven platform to visually design and manage cloud infrastructure, collaboratively.
It's the only solution that automatically generates IaC code for any cloud provider, with an embedded CI/CD.