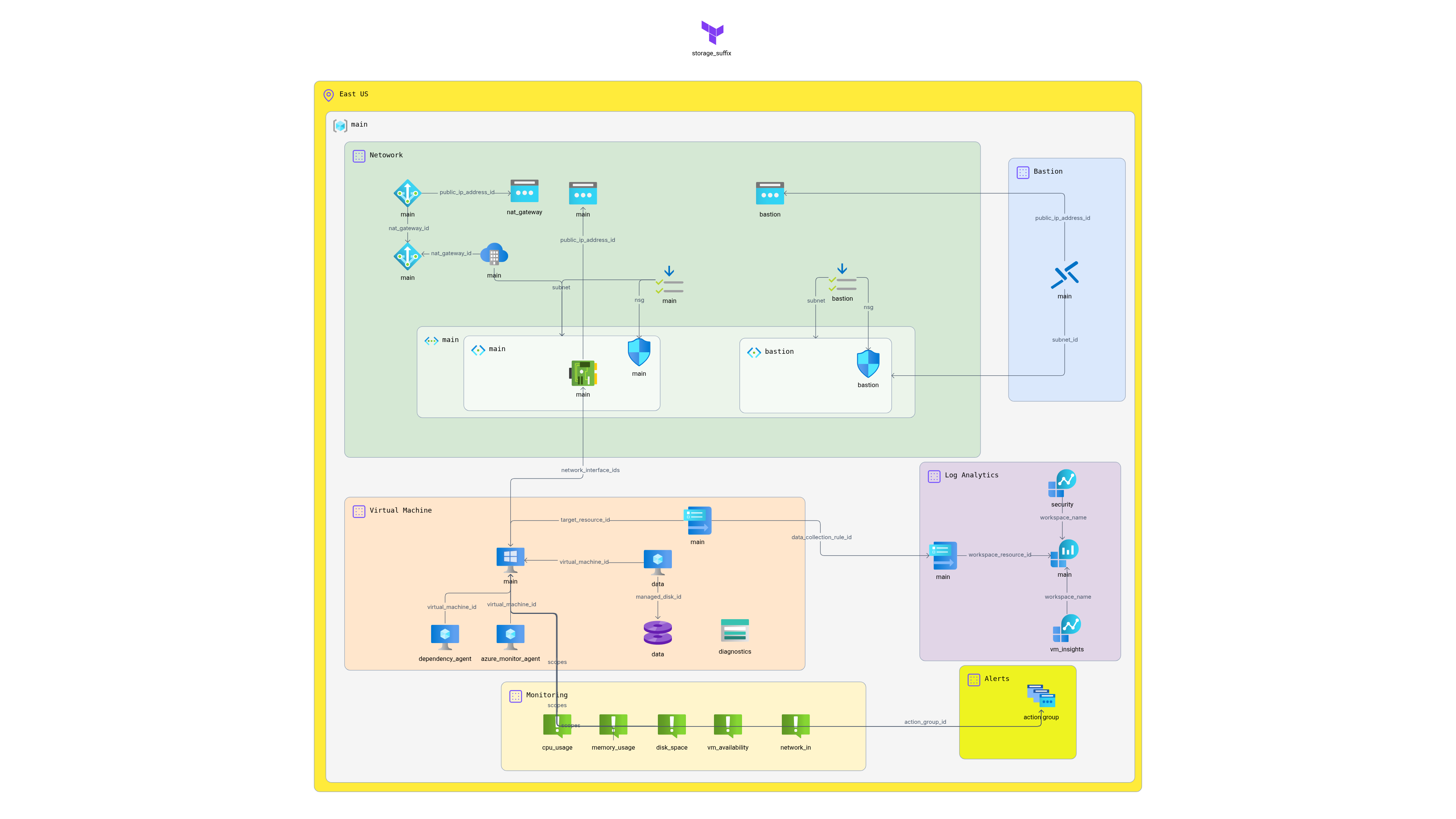
This Terraform configuration deploys a secure Windows VM architecture on Azure based on Microsoft's reference architecture for running a Windows VM on Azure.
## Architecture Overview
This configuration creates:
- **Resource Group**: Logical container for all resources
- **Virtual Network**: Isolated network environment with subnets
- **Network Security Groups**: Firewall rules for network security
- **Virtual Machine**: Windows Server VM with managed disks
- **Azure Bastion**: Secure access to VMs without public IPs (optional)
- **NAT Gateway**: Outbound internet connectivity (optional)
- **Storage Account**: For boot diagnostics (optional)
## Prerequisites
- Azure CLI configured and authenticated
- Terraform installed (>= 1.2)
- Valid Azure subscription with appropriate permissions
## Project Structure
```
├── provider.tf # Terraform and Azure provider configuration
├── locals.tf # Local values and naming conventions
├── variables.tf # Input variable declarations
├── terraform.tfvars # Variable values (customize for your environment)
├── main.tf # Core Azure resources
└── README.md # This file
```
## Resource Connections
- **VM → App Service Plan**: VM uses the specified size and configuration
- **VM → Virtual Network**: VM is deployed in the main subnet
- **VM → Network Security Group**: NSG rules control traffic to/from VM
- **VM → Managed Disks**: OS disk and data disk attached to VM
- **Bastion → Bastion Subnet**: Bastion requires dedicated subnet
- **NAT Gateway → Main Subnet**: Provides outbound internet connectivity
- **Network Interface → Public IP**: Only when Bastion is disabled
## Configuration Options
### Security Models
**Option 1: High Security with Azure Bastion (Recommended)**
```hcl
enable_bastion = true
enable_nat_gateway = true
allowed_source_addresses = ["203.0.113.0/24"] # Your office IP range
```
**Option 2: Direct Access (Less Secure)**
```hcl
enable_bastion = false
enable_nat_gateway = true
allowed_source_addresses = ["YOUR.IP.ADDRESS.HERE/32"]
```
### VM Sizing Options
- **Development**: `Standard_D2s_v3` (2 vCPUs, 8 GB RAM)
- **Production**: `Standard_D4s_v3` (4 vCPUs, 16 GB RAM)
- **High Performance**: `Standard_D8s_v3` (8 vCPUs, 32 GB RAM)
### Disk Performance Options
- **Standard_LRS**: Cost-effective for dev/test
- **StandardSSD_LRS**: Balanced performance and cost
- **Premium_LRS**: High performance for production workloads
## Usage
### 1. Clone and Initialize
```bash
# Navigate to your project directory
cd terraform-azure-windows-vm
# Initialize Terraform
terraform init
```
### 2. Customize Configuration
Edit `terraform.tfvars` to match your requirements:
```hcl
# Required: Update these values
project_name = "your-project-name"
environment = "dev"
location = "East US"
admin_password = "YourSecurePassword123!"
# Security: Update source IP addresses
allowed_source_addresses = [
"203.0.113.0/24" # Replace with your actual IP range
]
```
### 3. Plan and Deploy
```bash
# Review the execution plan
terraform plan -var-file="terraform.tfvars"
# Deploy the infrastructure
terraform apply -var-file="terraform.tfvars"
```
### 4. Access Your VM
**With Azure Bastion (Recommended):**
1. Navigate to Azure Portal
2. Go to your VM resource
3. Click "Connect" → "Bastion"
4. Enter your username and password
**With Direct RDP (if Bastion disabled):**
1. Get the public IP from Terraform output
2. Use Remote Desktop Connection
3. Connect to `:3389`
### 5. Post-Deployment Steps
1. **Initialize Data Disk**: Connect to VM and initialize the data disk
2. **Install Applications**: Deploy your applications to the data disk
3. **Configure Monitoring**: Set up Azure Monitor alerts if needed
4. **Apply Updates**: Install Windows updates and security patches
## Security Considerations
### Network Security
- Use Azure Bastion for secure access without exposing RDP ports
- Restrict `allowed_source_addresses` to specific IP ranges
- NSG rules follow principle of least privilege
### Data Protection
- OS and data disks use managed disks with encryption at rest
- Enable boot diagnostics for troubleshooting
- Regular backups recommended (not included in this template)
### Access Control
- Use strong passwords or Azure AD integration
- Consider implementing Just-In-Time (JIT) access
- Regular password rotation recommended
## Cost Optimization
### Development Environment
```hcl
vm_size = "Standard_B2s"
os_disk_type = "StandardSSD_LRS"
data_disk_type = "StandardSSD_LRS"
enable_bastion = false # Save costs if not needed
```
### Production Environment
```hcl
vm_size = "Standard_D4s_v3"
os_disk_type = "Premium_LRS"
data_disk_type = "Premium_LRS"
enable_bastion = true
```
## Monitoring and Maintenance
### Boot Diagnostics
- Enabled by default for troubleshooting boot issues
- Stored in dedicated storage account
### Recommended Monitoring
- Azure Monitor for VM metrics
- Log Analytics for centralized logging
- Azure Backup for data protection
## Troubleshooting
### Common Issues
**VM won't start:**
- Check boot diagnostics in storage account
- Verify VM size is available in selected region
**Can't connect via RDP:**
- Verify NSG rules allow traffic from your IP
- Check if Bastion is enabled and configured correctly
**High costs:**
- Review VM size selection
- Consider using B-series for variable workloads
- Deallocate VMs when not needed
### Useful Commands
```bash
# Check VM status
az vm show -g -n --show-details
# Start/Stop VM
az vm start -g -n
az vm deallocate -g -n
# Get VM public IP
terraform output vm_public_ip
```
## Cleanup
To remove all resources:
```bash
terraform destroy -var-file="terraform.tfvars"
```
## Support and Contribution
For issues and improvements:
1. Check Azure documentation for VM best practices
2. Review Terraform Azure provider documentation
3. Validate configuration with `terraform validate`
4. Use `terraform plan` to preview changes before applying
## References
- [Azure VM Reference Architecture](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/reference-architectures/n-tier/windows-vm)
- [Azure Bastion Documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/bastion/)
- [Terraform Azure Provider](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/azurerm/latest/docs)
Industries
.webp) HealthcareControl environments and simplify operations
HealthcareControl environments and simplify operations.webp) FinancialFragmentation leads to increased costs, inefficiency and risk
FinancialFragmentation leads to increased costs, inefficiency and risk.webp) RetailUnify financial operations to reduce risk and costs
RetailUnify financial operations to reduce risk and costs TelecommunicationSimplify network complexity and accelerate service delivery
TelecommunicationSimplify network complexity and accelerate service delivery GovernmentSecure, compliant, and efficient cloud adoption for the public sector
GovernmentSecure, compliant, and efficient cloud adoption for the public sector
Use cases
.webp) Move to IaCThe easiest way to move to IaC: Brainboard one click migration.
Move to IaCThe easiest way to move to IaC: Brainboard one click migration..webp) Standardize IaCGive your users a reason to follow your guidelines.
Standardize IaCGive your users a reason to follow your guidelines..webp) Self-serve modelBuild your internal service catalog to easily provision on-demand infrastructure.
Self-serve modelBuild your internal service catalog to easily provision on-demand infrastructure..webp) Lower the learning curveYou don’t need to learn everything at once. Learn by doing.
Lower the learning curveYou don’t need to learn everything at once. Learn by doing..webp) Your Disaster Recovery strategySystems fail, all the time. Plan ahead and protect against the unknown today!
Your Disaster Recovery strategySystems fail, all the time. Plan ahead and protect against the unknown today!
Features
- Smart cloud designerThe power of design combined with the flexibility of code
- Terraform & OpenTofu modulesCentral & single source of truth of your private, public and/or community modules.
- GitOps workflowSmoothly connect your cloud infrastructure with your git repository.
- Drift detection and remediationMonitor and maintain control of any drift between your source of truth and your cloud provider.
- Synchronized architecturesEliminate drift between your environments (dev, QA, staging, prod…)

Brainboard is an AI driven platform to visually design and manage cloud infrastructure, collaboratively.
It's the only solution that automatically generates IaC code for any cloud provider, with an embedded CI/CD.