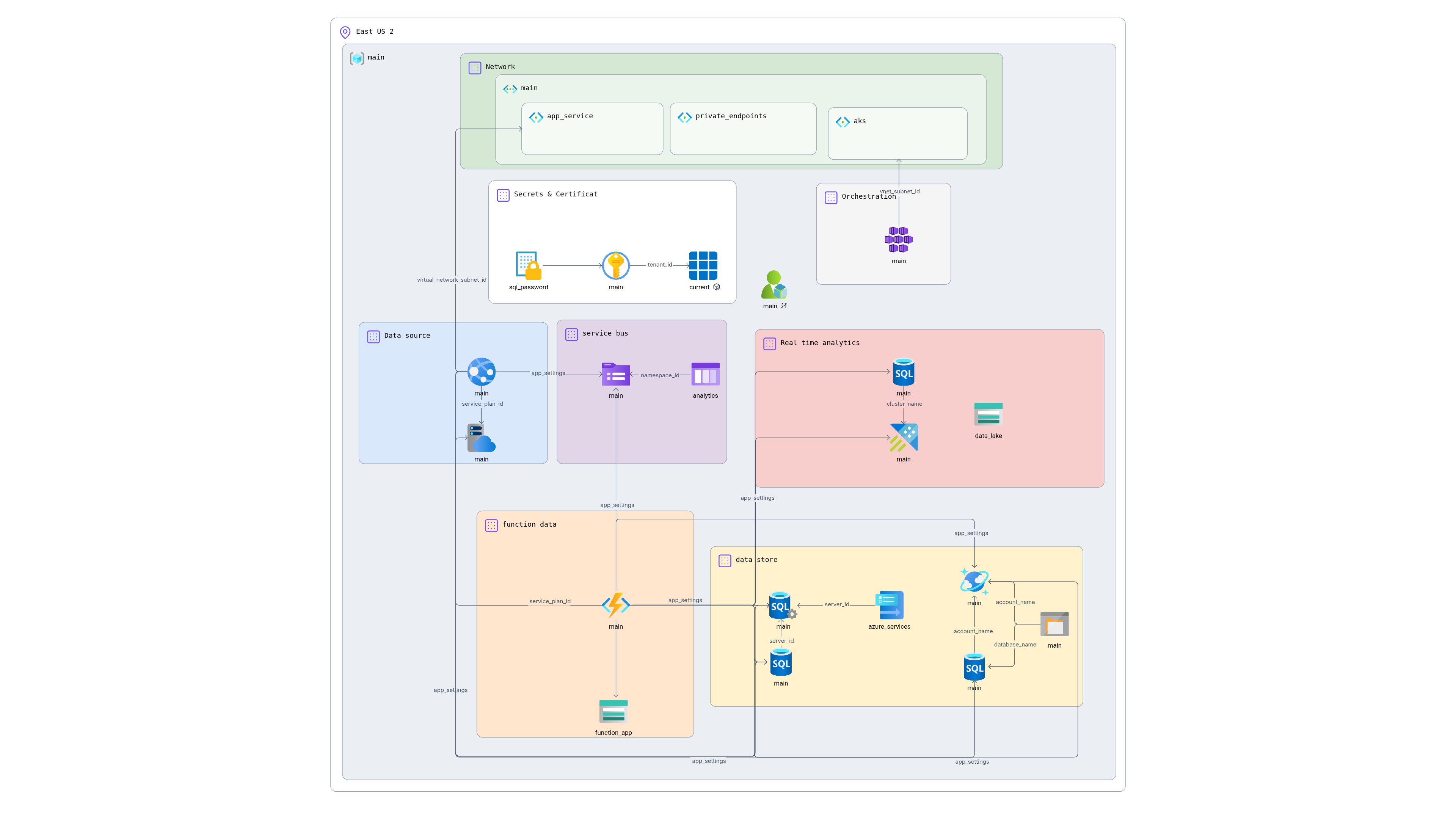
# Terraform: Azure Real-time Analytics Architecture with Service Bus
This Terraform configuration deploys a comprehensive Azure real-time analytics solution based on the [Azure Architecture Center reference](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/solution-ideas/articles/analytics-service-bus).
## Architecture Overview
The solution implements a real-time analytics pipeline using Azure Service Bus as the central message broker, enabling both operational data processing and near real-time analytics on the same data stream.
### Architecture Components
1. **Data Source**: Azure App Service hosting an OLTP application
2. **Message Broker**: Azure Service Bus for reliable message queuing
3. **Orchestration**: Azure Functions and AKS for data processing
4. **Operational Storage**: SQL Database and Cosmos DB for transactional data
5. **Analytics Engine**: Azure Data Explorer for real-time analytics
6. **Visualization**: Ready for integration with Power BI, Grafana, and Azure Data Explorer dashboards
7. **Additional Storage**: Data Lake Storage for long-term data retention
## Prerequisites
- Azure CLI configured and authenticated (`az login`)
- Terraform installed (>= 1.2)
- Appropriate Azure permissions to create resources
- Azure subscription with sufficient quotas
## Project Structure
```
├── provider.tf # Terraform and Azure provider configuration
├── locals.tf # Local values and naming conventions
├── variables.tf # Variable declarations
├── terraform.tfvars # Example variable values (customize for your environment)
├── main.tf # Main resource definitions
└── readme.md # This documentation
```
## Usage
### 1. Initialize Terraform
```bash
terraform init
```
### 2. Review and Customize Variables
Edit `terraform.tfvars` to match your requirements:
```bash
cp terraform.tfvars terraform.tfvars.local
# Edit terraform.tfvars.local with your specific values
```
**Important**: Change the SQL admin password and restrict IP ranges for security.
### 3. Plan the Deployment
```bash
terraform plan -var-file="terraform.tfvars.local"
```
### 4. Deploy the Infrastructure
```bash
terraform apply -var-file="terraform.tfvars.local"
```
### 5. Verify Deployment
After deployment, verify the resources in the Azure portal and test connectivity between components.
## Resource Connections and Data Flow
### Primary Data Flow
1. **App Service** → **Service Bus**: OLTP application sends events to Service Bus queue
2. **Service Bus** → **Function App** → **SQL Database/Cosmos DB**: Operational data processing
3. **Service Bus** → **Function App/AKS** → **Azure Data Explorer**: Real-time analytics processing
4. **Azure Data Explorer** → **Visualization Tools**: Data consumption for dashboards and reports
### Key Resource Dependencies
- **App Service** uses the App Service Plan's `service_plan_id`
- **Function App** references the same App Service Plan for cost optimization
- **Service Bus Queue** is created within the Service Bus Namespace
- **SQL Database** is hosted on the SQL Server with proper firewall rules
- **Cosmos DB Container** is created within the Cosmos DB Database
- **Azure Data Explorer Database** is created within the Kusto Cluster
- **AKS** is deployed within the dedicated subnet for network isolation
### Security and Access Control
- **Managed Identities**: All compute services use system-assigned managed identities
- **Role Assignments**:
- App Service has `Azure Service Bus Data Sender` role
- Function App has `Azure Service Bus Data Receiver` and Azure Data Explorer `Contributor` roles
- AKS has Azure Data Explorer `Contributor` and Service Bus receiver roles
- **Key Vault**: Stores sensitive configuration like SQL passwords
- **Network Security**: VNet integration for App Service and AKS subnet isolation
## Configuration Options
### Environment Scaling
For different environments, adjust these key variables:
**Development**:
```hcl
app_service_plan_sku = "S1"
kusto_cluster_sku_name = "Dev(No SLA)_Standard_D11_v2"
aks_node_count = 2
```
**Production**:
```hcl
app_service_plan_sku = "P1v3"
kusto_cluster_sku_name = "Standard_D13_v2"
aks_node_count = 5
enable_private_endpoints = true
```
### Security Hardening
For production deployments:
1. Enable private endpoints: `enable_private_endpoints = true`
2. Restrict IP ranges in `allowed_ip_ranges`
3. Use Azure Key Vault for all secrets
4. Configure network security groups and firewall rules
5. Enable Azure Monitor and diagnostic settings
## Post-Deployment Steps
### 1. Configure Application Code
Deploy your application code to:
- **App Service**: Your OLTP application that sends data to Service Bus
- **Function App**: Functions to process Service Bus messages and send to Azure Data Explorer
- **AKS**: Optional microservices for advanced data processing
**Cosmos DB Configuration**:
Your applications will find these environment variables:
```csharp
// .NET example
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CosmosDbEndpoint");
var key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CosmosDbKey");
var databaseName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CosmosDbDatabaseName");
var client = new CosmosClient(endpoint, key);
```
### 2. Set Up Azure Data Explorer
Configure Azure Data Explorer:
```kusto
// Create tables for your data
.create table Events (
Timestamp: datetime,
EventType: string,
UserId: string,
Data: dynamic
)
// Create ingestion mappings
.create table Events ingestion json mapping "EventsMapping"
'['
' {"column":"Timestamp","path":"$.timestamp","datatype":"datetime"},'
' {"column":"EventType","path":"$.eventType","datatype":"string"},'
' {"column":"UserId","path":"$.userId","datatype":"string"},'
' {"column":"Data","path":"$.data","datatype":"dynamic"}'
']'
// Create external table to Data Lake Storage (if needed)
.create external table ExternalEvents (
Timestamp: datetime,
EventType: string,
Data: dynamic
)
kind=blob
dataformat=json
(
h@'https://[storage-account].blob.core.windows.net/events'
)
```
### 3. Configure Visualization
Connect your preferred visualization tools:
- **Power BI**: Use Azure Data Explorer connector
- **Grafana**: Configure Azure Data Explorer data source
- **Azure Data Explorer Dashboards**: Create dashboards directly in ADX
### 4. Verify Role Assignments
The following permissions are automatically configured:
- All services can access their required resources via managed identities
- No connection strings needed - everything uses Azure RBAC
- Cross-service communication is secure and trackable
## Cost Optimization
- Use **Dev SKUs** for non-production environments
- Configure **auto-scaling** for App Service and AKS
- Implement **data retention policies** in Azure Data Explorer
- Use **reserved instances** for predictable workloads
- Monitor costs with **Azure Cost Management**
## Monitoring and Maintenance
### Key Metrics to Monitor
- Service Bus queue length and throughput
- Azure Data Explorer ingestion rates and query performance
- App Service and Function App performance metrics
- AKS cluster resource utilization
### Recommended Alerts
- Service Bus message backlog
- Azure Data Explorer failed ingestions
- App Service high response time
- SQL Database DTU utilization
## Troubleshooting
### Common Issues
1. **Service Bus Connection Issues**
- Verify managed identity role assignments
- Check that all role assignments were created successfully with `terraform state list | grep role_assignment`
2. **Cosmos DB Connection Issues**
- Applications should use `CosmosDbEndpoint` and `CosmosDbKey` environment variables
- Don't use connection strings - construct them in your application code
3. **Azure Data Explorer Ingestion Failures**
- Verify data format and mapping
- Check cluster capacity and throttling
- Ensure Function App has proper permissions
4. **Network Connectivity Issues**
- Ensure AKS service CIDR (172.16.0.0/16) doesn't conflict with your VNet (10.0.0.0/16)
- Verify subnet delegations are correct
- Check NSG rules if using private endpoints
5. **Role Assignment Issues**
- All role assignments are managed by a single resource with `for_each`
- To debug: `terraform state show azurerm_role_assignment.main[\"function_app_servicebus\"]`
## Technical Improvements
This configuration includes several optimizations over standard deployments:
### **Simplified Role Management**
- **Single Resource Block**: All 16 role assignments managed by one `for_each` loop
- **Dynamic Logic**: Automatic service and resource detection based on naming patterns
- **Easy Extension**: Add new permissions by updating `locals.tf` only
### **Enhanced Security**
- **Separate Credentials**: Cosmos DB uses endpoint/key instead of connection strings
- **Network Isolation**: Proper CIDR separation between VNet and AKS services
- **Managed Identities**: No connection strings stored in app settings where possible
### **Improved Maintainability**
- **Centralized Configuration**: All role assignments defined in `locals.tf`
- **Consistent Naming**: Predictable resource names across all environments
- **Reduced Duplication**: DRY principle applied to role assignments
## Cleanup
To destroy the infrastructure:
```bash
terraform destroy -var-file="terraform.tfvars.local"
```
**Warning**: This will permanently delete all resources and data. Ensure you have backups if needed.
## Support and Contributing
For issues or improvements:
1. Check Azure Data Explorer and Service Bus documentation
2. Review Terraform Azure provider documentation
3. Consult Azure Architecture Center for best practices
## Additional Resources
- [Azure Data Explorer Documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-explorer/)
- [Azure Service Bus Documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-bus-messaging/)
- [Azure Architecture Center](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/)
- [Terraform Azure Provider](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/azurerm/latest/docs)
Industries
.webp) HealthcareControl environments and simplify operations
HealthcareControl environments and simplify operations.webp) FinancialFragmentation leads to increased costs, inefficiency and risk
FinancialFragmentation leads to increased costs, inefficiency and risk.webp) RetailUnify financial operations to reduce risk and costs
RetailUnify financial operations to reduce risk and costs TelecommunicationSimplify network complexity and accelerate service delivery
TelecommunicationSimplify network complexity and accelerate service delivery GovernmentSecure, compliant, and efficient cloud adoption for the public sector
GovernmentSecure, compliant, and efficient cloud adoption for the public sector
Use cases
.webp) Move to IaCThe easiest way to move to IaC: Brainboard one click migration.
Move to IaCThe easiest way to move to IaC: Brainboard one click migration..webp) Standardize IaCGive your users a reason to follow your guidelines.
Standardize IaCGive your users a reason to follow your guidelines..webp) Self-serve modelBuild your internal service catalog to easily provision on-demand infrastructure.
Self-serve modelBuild your internal service catalog to easily provision on-demand infrastructure..webp) Lower the learning curveYou don’t need to learn everything at once. Learn by doing.
Lower the learning curveYou don’t need to learn everything at once. Learn by doing..webp) Your Disaster Recovery strategySystems fail, all the time. Plan ahead and protect against the unknown today!
Your Disaster Recovery strategySystems fail, all the time. Plan ahead and protect against the unknown today!
Features
- Smart cloud designerThe power of design combined with the flexibility of code
- Terraform & OpenTofu modulesCentral & single source of truth of your private, public and/or community modules.
- GitOps workflowSmoothly connect your cloud infrastructure with your git repository.
- Drift detection and remediationMonitor and maintain control of any drift between your source of truth and your cloud provider.
- Synchronized architecturesEliminate drift between your environments (dev, QA, staging, prod…)

Brainboard is an AI driven platform to visually design and manage cloud infrastructure, collaboratively.
It's the only solution that automatically generates IaC code for any cloud provider, with an embedded CI/CD.